The ongoing struggle to control burgeoning and herbicide-resistant black-grass populations is well documented, and is fight that many UK growers are all too familiar with.
Unfortunately, black-grass isn't the only herbicide-resistant grass weed that growers are battling, with an increasing number of agronomists reporting difficulties in controlling ryegrass infestations.
We take a look at the current situation facing UK growers, and – in conjunction with our in-season updates (click here to subscribe) – highlight some key points of action growers can take to reduce the ryegrass pressure in arable crops.

Ryegrass is a common arable weed in many parts of the UK, with Italian ryegrass (Lolium multiflorum) prevalent in the Midlands and the South of the UK and typically more problematic than Perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne).
One of the key reasons for the prevalence of Italian ryegrass is the simple fact that its seed can survive in soil seedbanks for extended periods (in excess of five years in the right conditions).
Ryegrass is also exceptionally vigorous and is actually more competitive than black-grass: a population of just five plants/m2 can typically cause a yield loss of 5% in cereals, with higher infestation rates known to cause losses of up to 89%.
Ryegrass also tillers more profusely than black-grass, with each plant commonly producing over 20 heads and 5,000 seeds. As a result, populations can build up very rapidly.
Herbicide-resistant Italian ryegrass was first detected in the UK in 1990 and it is now present on more than 475 farms in 33 counties in England. In comparison, herbicide-resistant black-grass was known to be present on 20,000 farms in 35 counties in 2017, so although the ryegrass problem is relatively new, it is an increasingly significant cause for concern, especially as resistance to ALS inhibitors was confirmed in 2012.
As is the case in black-grass, ryegrass is affected by both target site and non-target site resistance (NTSR) or enhanced metabolism resistance mechanisms. The main threat seems to be from enhanced metabolism mechanisms which can reduce the efficacy of a wide range of herbicide actives.
ACCase (FOP, DIM and DEN) and ALS (e.g. sulfonylurea) target site resistance have both been confirmed in ryegrass, but at present this resistance is much less frequent compared to black-grass.
Although herbicide resistance is currently less of an issue in ryegrass compared to black-grass, there is no room for complacency because ryegrass species globally have shown cross-resistance to 10 different herbicide modes of action in at least 11 countries – more than for any other weed.
As the table below indicates, resistance can impact the efficacy of most of the main herbicide modes of action, with the severity and incidence of resistance varying depending on the mode of action.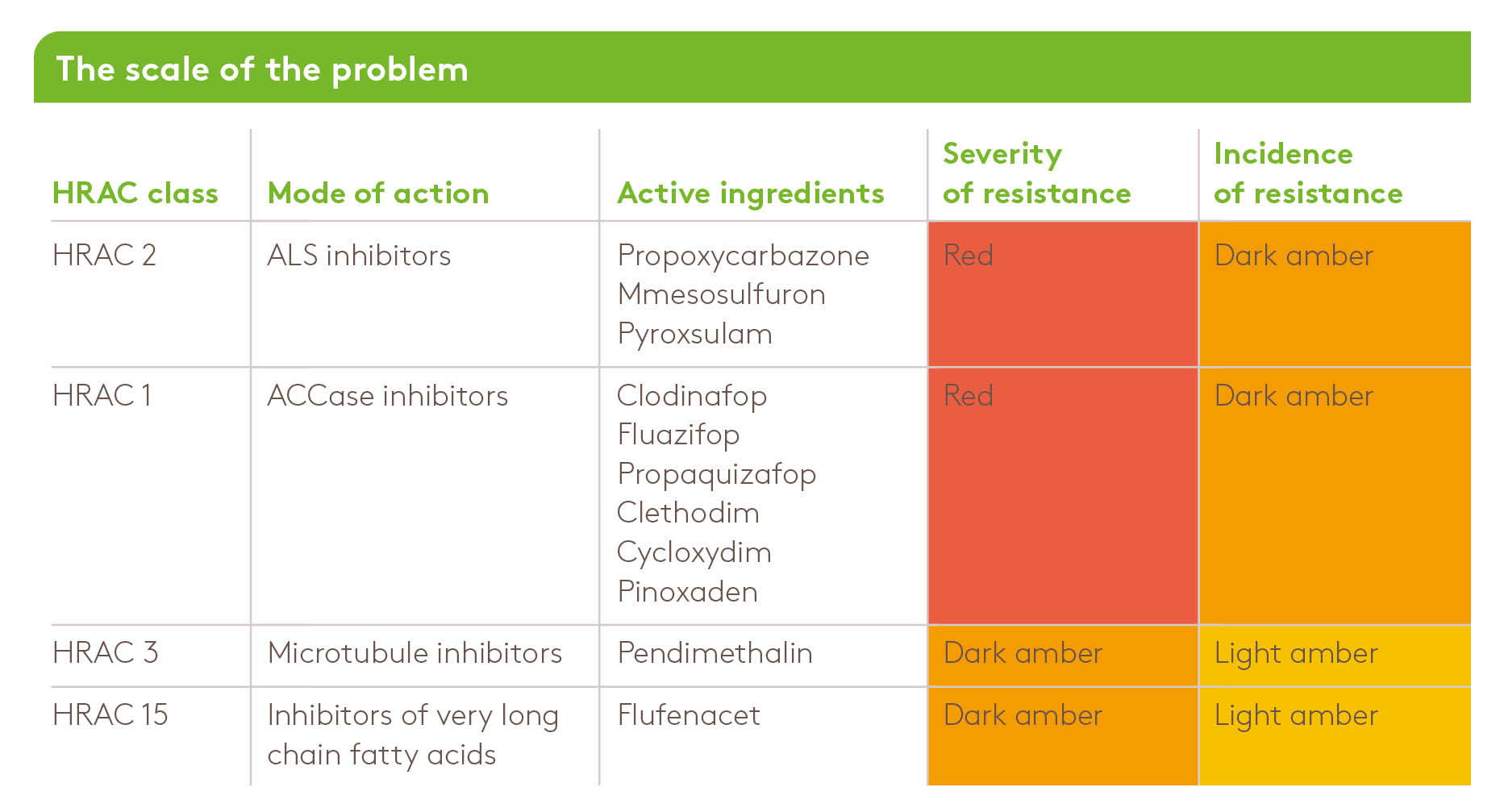
Key
Green = not recorded
Light Amber = low incidence or less severe
Dark Amber = high incidence and / or poor control with that ai
Red = Common and / or control failure with that ai
In order to reduce the risk of further resistance delveoping, and to protect the efficacy of existing herbicides, growers should use a combination of active ingredients with different modes of action: these should be deployed in a programme that stacks products in a sequenced approach beginning at the pre-emergence timing. For more information about which actives to use and when, please subscribe to our in-season updates.
A unique residual herbicide containing three active ingredients: pendimethalin, diflufenican and chlorotoluron. It is effective against black-grass when used in a programme and provides excellent standalone control of annual meadow-grass and broad-leaved weeds in winter and spring cereals.
Contains 250g/l chlorotoluron, 40g/l diflufenican and 300g/l pendimethalin.
A long-lasting and reliable residual herbicide containing pendimethalin. It provides a good foundation for control programmes targeted at tough grass and broad-leaved weeds in cereals.
Contains 400g/l pendimethalin.
A residual herbicide containing diflufenican. It is a key herbicide for the control of black-grass and can also be used to control a broad spectrum of broad-leaved weeds and annual meadow-grass. Hurricane® SC can be added to Herold® to improve black-grass control.
Contains 500g/l diflufenican.
A contact and residual broad spectrum herbicide containing the leading grassweed ingredient, flufenacet, plus diflufenican. When applied at 0.3l/ha, Herold delivers 120 gai/ha flufenacet and 60 gai/ha diflufenican, so is an excellent choice for the pre-emergence treatment.
Contains 400g/l flufenacet and 200g/l diflufenican.
A broad spectrum residual herbicide containing two active ingredients: diflufenican and pendimethalin. It is an excellent tank mix partner for the control of black-grass and wild oats and is also effective against broadleaved weeds in winter and spring cereals.
Contains 40g/l diflufenican and 400g/l pendimethalin.
Spinnaker is used for the control of annual grassweeds and annual broad-leaved weeds in winter barley, winter wheat and early and maincrop potatoes.
Contains 800 g/l prosulfocarb.
Understanding and combating the threat posed by ryegrass as a weed of arable crops
Overview:
https://ahdb.org.uk/understanding-and-combating-the-threat-posed-by-rye-grass-as-a-weed-of-arable-crops-phd
Full report: https://projectblue.blob.core.windows.net/media/Default/Research%20Papers/Cereals%20and%20Oilseed/2019%20(and%20earlier)/AHDB%20Student%20Report%2018.pdf
Weed control – Ryegrass threat looms: useful commentary on the latest Italian ryegrass resistance testing by NIAB
http://www.cpm-magazine.co.uk/2020/10/13/weed-control-ryegrass-threat-looms/
Herbicide resistance weeds by source of action, The International Survey of Herbicide Resistant Weeds
http://www.weedscience.org/Pages/SOASummary.aspx
Get the latest crop management advice and seasonal updates
Hear expert advice from the ADAMA team and wider agricultural community
Third Floor East 1410
Arlington Business Park
Theale
Reading
Berkshire RG7 4SA
United Kingdom
+44 1635 860 555
Email: ukadmin@adama.com
Enquiries: ukenquiries@adama.com